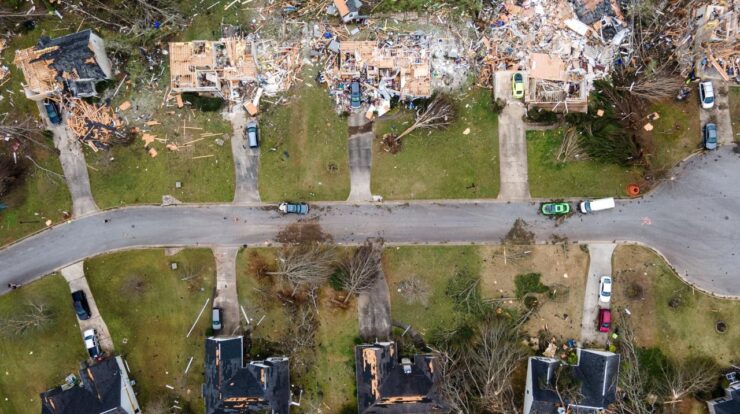
Tornadoes today pose a significant threat to communities across the United States. With the increasing frequency and intensity of these storms, it is crucial to understand their formation, prediction, and safety measures to mitigate their devastating impact.
Recent tornado outbreaks have left a trail of destruction, highlighting the urgent need for preparedness and education. Historical data reveals patterns and trends that help meteorologists forecast and track these storms, enabling timely warnings and evacuation procedures.
Tornado Activity and Trends
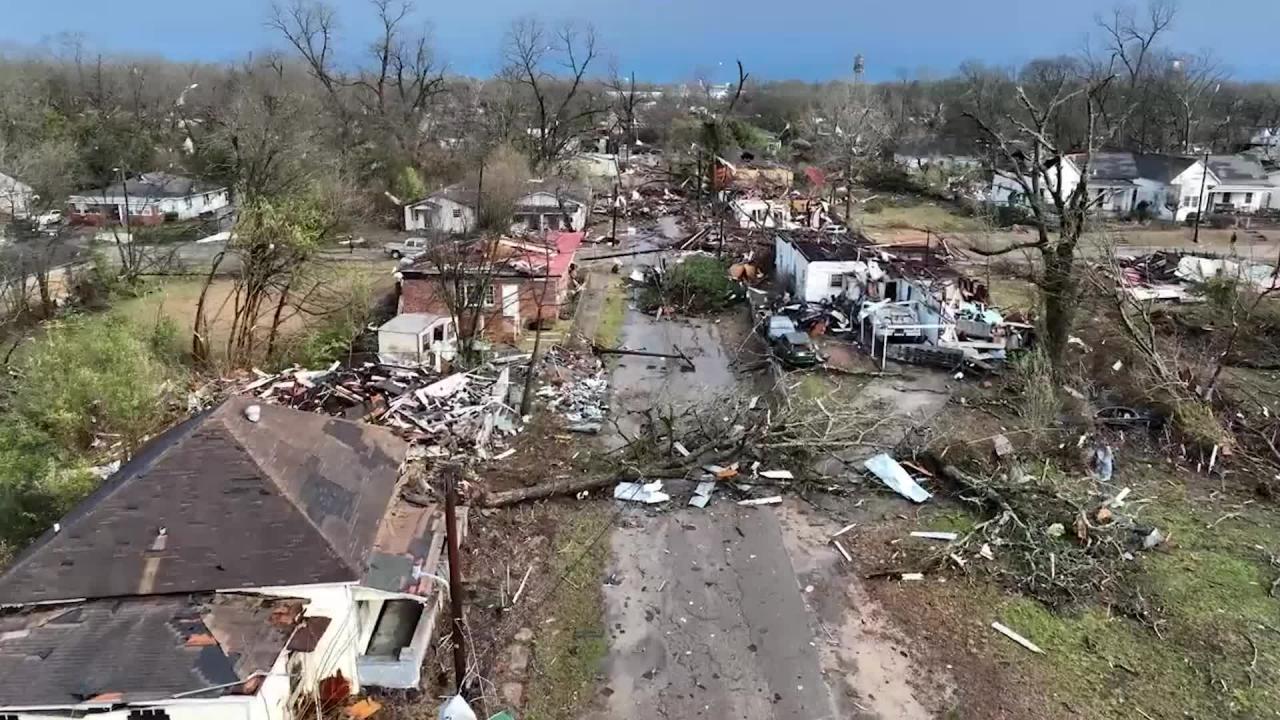

Tornadoes, violent rotating columns of air that extend from a thunderstorm to the ground, are a common occurrence in the United States. In recent years, tornado activity has been increasing in both frequency and intensity.
According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), there were 1,218 tornadoes reported in the United States in 2021, the highest number since 2011. The year also saw several major tornado outbreaks, including the deadly December 10-11 outbreak that killed 90 people and caused billions of dollars in damage across six states.
Historical Tornado Trends
- Tornado activity has been increasing in recent decades, with the average number of tornadoes reported each year rising from 875 in the 1990s to 1,238 in the 2010s.
- The increase in tornado activity is likely due to a number of factors, including climate change, which is leading to more frequent and intense thunderstorms.
Tornado Formation and Prediction: Tornadoes Today
Tornadoes form when warm, moist air from the Gulf of Mexico meets cold, dry air from the north. The rising warm air creates a rotating column of air, which can become a tornado if it becomes strong enough.
Types of Tornadoes
- Weak tornadoes (EF0-EF1) have wind speeds of up to 110 mph and can cause damage to trees and structures.
- Strong tornadoes (EF2-EF3) have wind speeds of up to 165 mph and can cause significant damage to buildings and infrastructure.
- Violent tornadoes (EF4-EF5) have wind speeds of over 165 mph and can cause catastrophic damage, including the complete destruction of buildings.
Predicting Tornadoes
Tornadoes are difficult to predict, but meteorologists use a variety of tools to track and forecast them. These tools include Doppler radar, which can detect the rotation of air within a thunderstorm, and satellite imagery, which can show the development of thunderstorms.
Tornado Safety and Preparedness
If you are in an area where tornadoes are common, it is important to have a tornado preparedness plan in place. This plan should include:
- A safe place to go during a tornado warning, such as a basement or interior room on the lowest floor of your home.
- A way to receive tornado warnings, such as a NOAA weather radio or a smartphone app.
- A plan for evacuating your home if necessary.
Staying Safe During a Tornado Warning, Tornadoes today
- If you are in a building, go to the lowest floor and find a windowless room or hallway.
- If you are outside, lie down in a ditch or other low-lying area and cover your head with your hands.
- Do not try to drive during a tornado warning.
Tornado Impact and Recovery
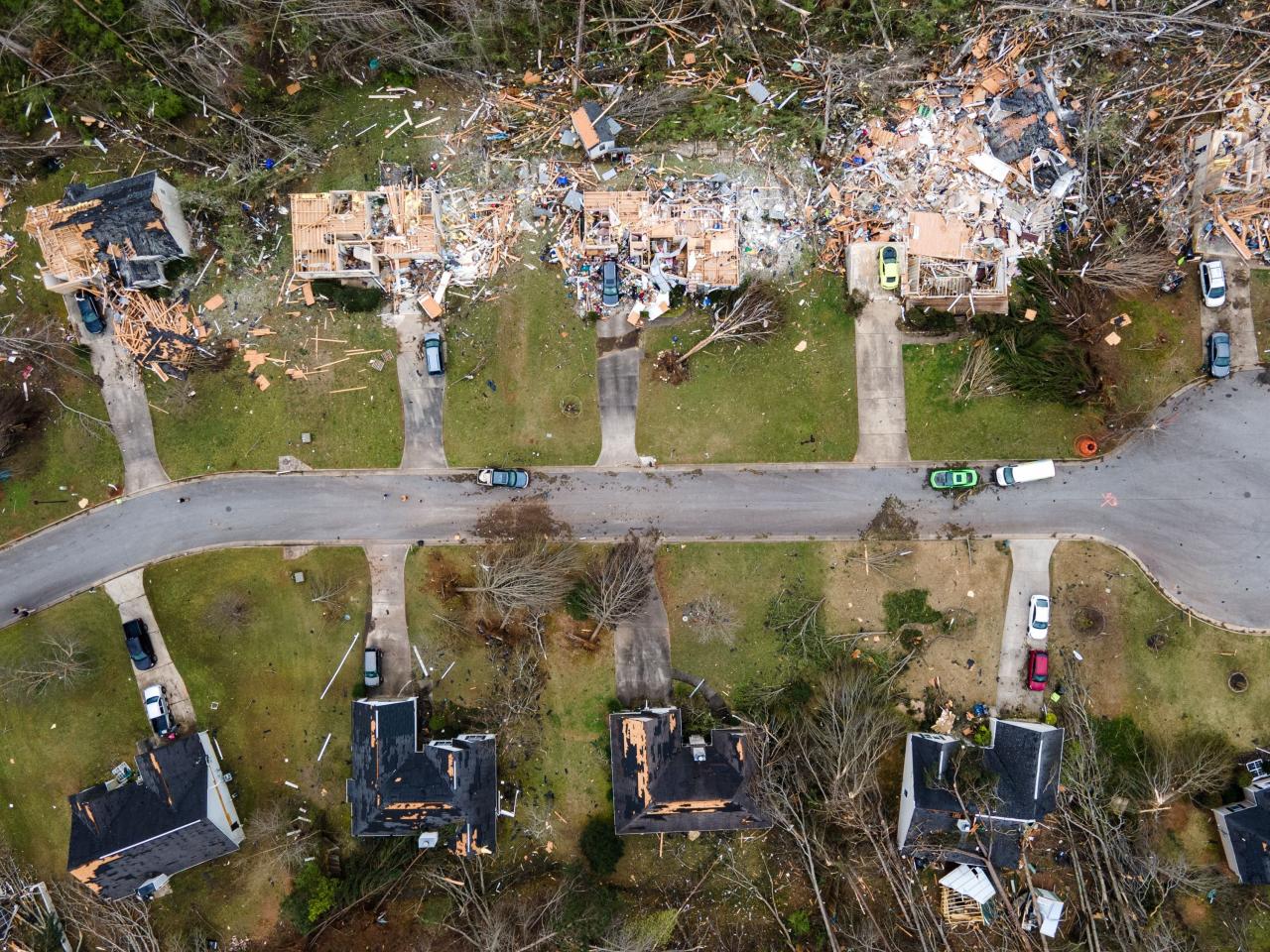

Tornadoes can have a devastating impact on communities. They can cause widespread damage to buildings and infrastructure, and they can also lead to loss of life. The recovery from a tornado can be a long and difficult process.
Challenges of Tornado Recovery
- The immediate aftermath of a tornado can be chaotic, with downed power lines, blocked roads, and damaged buildings.
- The recovery process can be slow and expensive, and it can take months or even years for a community to fully recover.
Resilience and Community Support
Despite the challenges, communities often come together in the aftermath of a tornado to help each other rebuild. This support can take many forms, from providing food and shelter to volunteering to help with cleanup and repairs.
Tornado Research and Mitigation
Scientists are constantly working to better understand tornadoes and to develop ways to mitigate their impact. This research includes:
- Studying the meteorological conditions that lead to tornado formation.
- Developing new technologies to detect and track tornadoes.
- Exploring ways to build tornado-resistant structures.
Role of Technology
Technology is playing an increasingly important role in tornado research and mitigation. Doppler radar and satellite imagery are now essential tools for tracking and forecasting tornadoes. And new technologies, such as artificial intelligence, are being developed to help scientists better understand tornadoes and to improve warning systems.
Wrap-Up
Understanding the science behind tornadoes and implementing effective safety strategies can save lives and reduce property damage. Ongoing research and technological advancements are paving the way for improved detection and warning systems, while innovative mitigation strategies aim to minimize the impact of these powerful storms.
FAQ Insights
What are the warning signs of a tornado?
Dark, rotating clouds, a funnel-shaped cloud extending from the base of a cloud, and loud, roaring noises are all signs of a potential tornado.
What should I do if I am caught in a tornado?
Seek shelter immediately in a sturdy building or underground. If outdoors, lie flat in a ditch or low-lying area and cover your head with your hands.
How can I prepare for a tornado?
Have a tornado preparedness plan in place, including designated safe rooms, evacuation routes, and emergency supplies. Stay informed about weather forecasts and be ready to take action if a tornado warning is issued.